Introduction-
The debate between hemp and cotton has emerged as one of the most talked about issues of sustainable fashion. The two materials are natural and breathable and are common in the wearing of clothes and domestic textile. However, they vary in the way they are cultivated, processed and even worn.
Comfort, durability, and environment are some of the aspects of the current consumer that are of concern. With individuals trying to find sustainable alternatives, hemp has returned to be a worthy competitor to cotton. In this article, we will see the performance of both the fabrics in the softness, strength and sustainability. The idea is to make you be informed in an environmentally-conscious decision.
What is Hemp Fabric?
Hemp Fibers

Hemp Plant
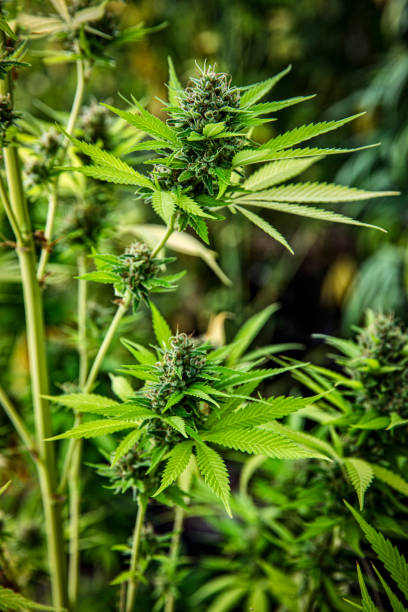

Origin
The hemp cloth is made of Cannabis sativa. It is a bast fiber, i.e. that the textile fibers are located in the bark of the stalk. The thick fibers of the stem are pulled off and woven into a fiber. Hemp is fast growing and has naturally resistant fibers, hence it does not require pesticides or fertilizers. In a nutshell, hemp fabric is made out of the outer stalk fiber of the hemp plant, not the leaves and flowers.
Key Properties
- Strength: Hemp is very powerful. Its fibers are up to five times stronger as compared to cotton. Consequently, hemp fabric has high resistance against wear and tear, moulds and mildew, which gives the garments a very extended life cycle.
- Breathability: Hemp has a good breath. It has porous hollow fibers that wick the moisture and allow airflow. This implies that hemp clothing remains cool during the summer seasons and warm during the winter seasons and it dries fast.
- Antimicrobial: Hemp has natural antimicrobial and antifungal. It is also bacteria and odor resistant which makes it suitable in sensitive skin and activewear.
History of Use
Hemp has a rich history. It was nurtured in ancient China several millennia ago to produce textiles, paper and ropes. Sailors also now had to rely on hemp fiber which was used to provide powerful ropes and sailcloth to ships. In the past centuries, hemp was a common crop, which was widely used and cultivated in Asia, Europe and the Americas. Hemp textiles are having a resurgence today as people reevaluate this miracle fiber that is said to be strong and environmentally friendly. The history of hemp as a durable fabric manufacturer is an additional factor that supports the idea of hemp as a sustainable material.

What is Cotton Fabric?
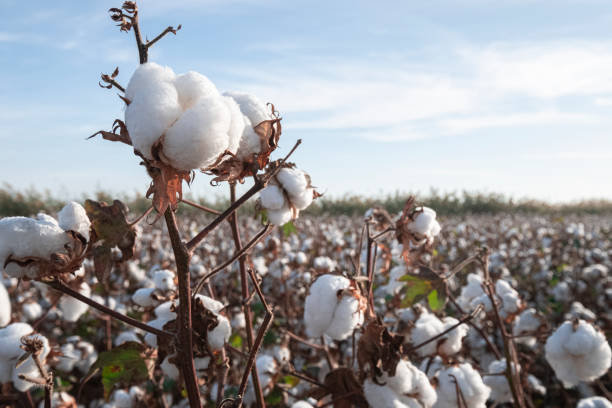

Origin
The fluffy fibers of cotton plant seeds are cut into cotton fabric. Cotton plant (genus Gossypium) is a plant that is grown with soft and white fibers in protective seed pods known as bolls. The bolls are harvested and processed by farmers to extract the fiber and the seeds. Cotton fibers are cellulose practically pure and have been spun into yarn thousands of years. Concisely, cotton does not grow out of the wood or the leaves of the cotton plant but out of the seed hairs.
Key Properties
- Softness: Cotton is also known as naturally soft and comfortable. It is soft on the skin and is commonly applied on clothing that comes in direct contact with the skin.
- Breathability: Cotton is very breathable and it lets the air circulate around the body. Its fibers are easy to absorb moisture and that is why cotton clothes feel cool and comfortable during warm weather.
- Absorbency: Cotton is a material that is excellent at absorbing liquids. It evaporates sweat and moisture very easily and this keeps the skin dry. This high absorbency however implies that cotton is able to retain dampness when it is unable to dry off.
Global Dominance
Cotton is the natural fiber that has the broadest applications on earth. Every year millions of tons of cotton are cultivated. The fashion and textile industries around the globe are run by it, driving the goods as T-shirts and jeans as well as bedding and towels. The scale of production of cotton makes it very cheap and accessible in virtually any market. Due to its hegemonic position around the world, cotton vs hemp tends to turn into a matter of expediency vs sustainability.
Hemp vs Cotton: Key Differences
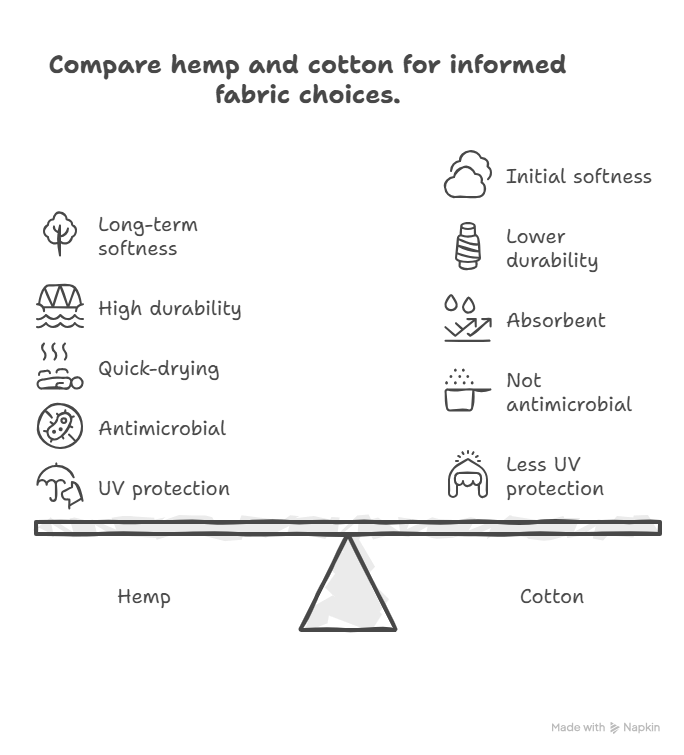
Softness & Comfort
Cotton is softer initially. Its small fibers are smooth and comfortable on the first day. On the contrary, hemp fabric begins rougher. But hemp grows soft as time and use. Its long fibers rupture gradually, and they grow malleable without diminishing their power. Finally, cotton prevails on short term softness, but hemp keeps up in the long term with repeated use. Hemp might be hard at the beginning, but becomes as comfortable after a few washes.
Durability
Hemp is much more resistant compared to cotton. A hemp garment has high tensile strength and this allows it to sustain many years compared to a cotton garment. Hemp is tear resistant, abrasive and pilling resistant. Hemp clothing does not lose its shape and strength after numerous washes. Conversely, the cotton fibers are very much likely to weaken with time. Fabrics made out of cotton become skinny when used and washed severally. To recap it all, hemp is far more durable than cotton: a T-shirt made of hemp could easily be twice as long as the cotton T-shirt.
Moisture & Breathability
These two fabrics are breathable and ensure that you are comfortable in the warm weather. Cotton is absorbent and may get wet due to sweat and thus in humid weather make the cloth sticky. Hemp also pulls moisture off and it dries much quicker. The hollow fibers of Hemp permit better airflow and rapid evaporation. Consequently, hemp garments are more likely to be drier and cooler when you sweat as compared to cotton. Simply put, the two are breathable, however, the hemp has a slight advantage when it comes to remaining dry and maintaining temperature.
Hypoallergenic/Antimicrobial
Hemp possesses an inherent antimicrobial attribute. The specialized substances of hemp fibers prevent bacteria, fungi, and smell. This renders the hemp fabric hypoallergenic and suitable to sensitive skin. Cotton on the other hand, is not microbe-resistant in nature. Generally, it is deemed as being mild on the skin, however, it does not give the same type of antibacterial protection that hemp provides. This, in reality, implies that hemp clothing has a longer shelf life, whereas in hot weather, cotton can be used more often.
UV Protection
Hemp is far better in blocking ultraviolet (UV) rays as compared to cotton. Growing hemp fibers naturally block the sun and therefore makes a great fabric to be worn in the outdoors. As a matter of fact, the hemp has the ability to block above 99% of UVB rays and UVA rays. Cotton is more permeable to UV and it fades faster in the sun. Hemp has significantly greater sun protection and color retention, particularly in the hottest climates, and when used as an outdoor garment, than cotton.
| Feature | Hemp Fabric | Cotton Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Softness & Comfort | Starts rough but softens over time; durable, breathable | Naturally soft from the start; very comfortable initially |
| Durability | Extremely strong and long-lasting; resists wear, tearing, mildew | Moderate; good quality cotton is strong, but fibers wear thin faster |
| Moisture & Breathability | Very breathable with excellent moisture-wicking; stays dry and cool | Very breathable with high absorbency; absorbs sweat but can feel damp |
| Antimicrobial | Naturally antibacterial and odor-resistant | Lacks natural antimicrobial properties; absorbs bacteria and odors |
| (No inherent protection) | ||
| UV Protection | Excellent UV resistance; blocks ~99% of harmful rays | Good, but more prone to UV fading |
Environmental Impact: Hemp vs Cotton
Water Use
Cotton is highly water consuming. Farmers require a very large quantity of irrigation to cultivate and process cotton. To take a scenario, it takes approximately 10,000 liters of water to produce 1 kg of cotton, and that is equivalent to around 2,500 liters to produce one T-shirt. In comparison, hemp requires a lot less water. Hemp can grow with rain but as little as 300500 liters of water are required to produce 1 kg of fiber. Realistically, the water footprint of hemp is much smaller than that of cotton by at least 1/3 in certain research. This enormous gap is what renders hemp a more environment-friendly option in the areas where there is a shortage of water.
Pesticides & Chemicals
Traditional cotton cultivation is dependent on chemicals. It uses approximately 16 percent of the insecticides and 7 percent of all pesticides in the world. The chemicals may contaminate waterways and destroy ecosystems. Hemp, on the contrary, is resistant to pests. It needs minimal or no pesticides and herbicides in its production. Hemp farmers have decades of experience of growing hemp with virtually no uses of chemicals. In general, the low-chemical profile of hemp compared to the extensive use of pesticides in cotton provides hemp with an obvious environmental benefit.
Land Use & Yield
Hemp also utilizes less land. One acre of hemp has the potential to produce approximately 2,500-3,000 pounds of the dry fiber. An acre of cotton yields, comparatively, but 1,200 to 1,500 pounds of cotton lint. That is, hemp usually yields almost two times the amount of fiber per acre compared to cotton. Such increased output implies that a smaller amount of land is required to make the same fabric. The deep-rooted hemp also enhances the soil structure and prevents soil erosion as compared to cotton which can drain the soil of its nutrients.
Sustainability Score
Collectively, hemp usually comes out as more sustainable than cotton. Hemp is a very friendly crop as it requires low water, minimal pesticides, it yields a lot, and it improves soil. The environmental effect of cotton is greater because of the resource consumption and the usage of chemicals. Overall, the majority of the analysis indicates that hemp was considered to be the greener option in the production of fabric.
Cost & Availability
Cotton
Cotton is still one of the cheapest natural fabrics in the world textile sector. It is highly cultivated in large scopes and has well-developed supply chains which make it easily available everywhere. Cotton products can be found in almost all price ranges, starting with simple T-shirts and ending with the luxurious bedding.
Hemp
The cost of hemp fabric is now priced higher because there is a lack of large-scale manufacture as well as processing requirements. It is still under regulation in certain countries and this limits supply and increases the cost. Nevertheless, due to the emergence of sustainable fashion, an increasing number of brands invest in hemp, which reduces its price.
Blended Fabrics
In order to achieve a balance between the comfort, strength and affordability many companies are currently using hemp mixed with cotton fibers. Such mixed fabrics are soft, durable and have less environmental impact as opposed to pure cotton. They are an effective alternative to sustainable, yet affordable textiles to the consumers.
Best Uses for Hemp vs Cotton
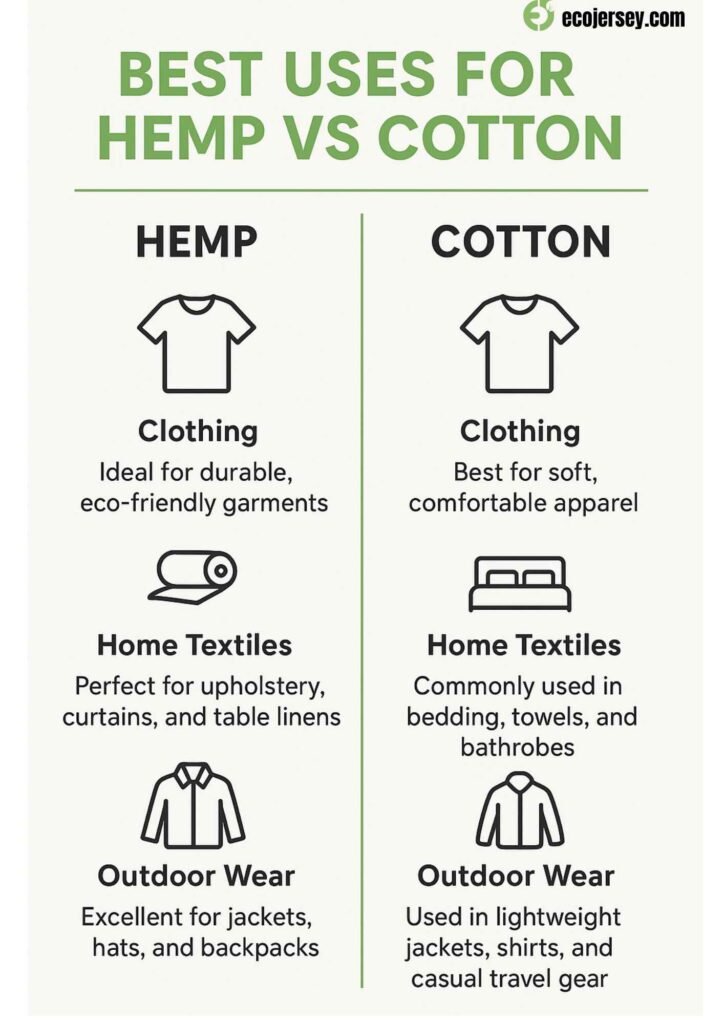
Clothing
Mainstream clothing is dominated by cotton. It is available in T-shirts and underwear as well as dresses and casual wear as it feels soft and is cheap. Hemp fiber clothes are generally found in small-scale eco-fashion. Sustainable brands tend to use hemp to make clothing such as casual clothes, jeans, and jackets. The breathability and strength of hemp render it an activewear and a comfortable everyday wear particularly when blended with other softer fibers.
Home Textiles
Cotton is king when it comes to bedding and towels to be used at home. A majority of sheets, pillow cases, towels and washcloths are comprised of cotton which is highly valued because of its softness and absorbency. Home use of hemp is also possible: the high level of absorbency, antimicrobial properties turn the hemp into the perfect cotton towel, table cloth, and dish cloth. This is also being utilized in heavy-duty household fabrics such as canvas, rugs and upholstery where its strength and resistance to the UV is beneficial.
Outdoor Wear
Hemp is very strong and excellent in outdoor wear due to its water wicking capacity, UV protection and durability. In the case of hiking clothes, sun hats, and camping attire, hemp apparel will not be subject to sun rays and they will be quick drying. On the contrary, cotton outdoor garments have the ability to absorb water and become damp and loose. Thus, hemp will be better at gear that is used under harsh conditions and in the sun.
Pros & Cons of Hemp vs Cotton
- Hemp Advantages: Environmentally friendly and sustainable (uses less water/pesticides); exceptionally tough and strong; naturally antimicrobial and waterproof.
- Hemp Cons: roughness (however, it becomes soft after washing); its price is higher because of scarce supply; is not as widespread as cotton.
- Cotton Advantages: Soft, breathable, comfortable; highly versatile and popular, cheap and readily available in all types of outlets.
- Cotton Cons: Water consumption is very high and pesticides are also very heavily relied on; the cotton is highly dependent on intensive chemical applications; the fibers deteriorate much faster and this means that the cotton garments would have a shorter life span.
Organic Cotton vs Hemp – A Fairer Comparison?
Less Pesticides and Less Water.
Organic cotton gets rid of the majority of pesticides that are harmful and consumes much less water as compared to conventional cotton. It is morally sounder and more environmentally friendly.
Durability Factor
Hemp is long lasting even though organic cotton is sustainable. The fibres of hemp still beat the cotton in the durability tests.
Eco-Conscious and Ethical Choice.
Organic cotton and hemp both are in favor of sustainable fashion. Selecting one or the other one would be like encouraging responsible agriculture and minimizing your ecological footprint.
Conclusion-
The hemp vs cotton comparison indicates that the two fabrics have their own strengths. Cotton is immediately soft, cheap, and versatile. Hemp is unique in the sense that it is strong, sustainable, and comfortable in the long run.
Hemp is the choice in case you want to be sustainable. Cotton is also an excellent option in case the budget and immediate softness are the most important. The combination of the two materials is the best compromise, soft, durable, and eco-friendly.
Whether you prefer hemp or cotton is now a question of priorities, comfort now or a green world tomorrow.
FAQs
Is hemp fabric softer than cotton?
Cotton is softer to the touch. However, as time passes, hemp becomes softer with each wash and the disparity becomes smaller.
Which lasts longer, hemp or cotton?
Hemp lasts longer. High strength and durability make a hemp garment very easy to extend the life of a similar garment made of cotton.
Is hemp better than cotton for the environment?
Yes. Hemp normally consumes much less water, almost no pesticides, and enhances health of the soil. In general, the ecological footprint of hemp farming is less than that of traditional cotton.
Does hemp clothing shrink?
On the initial run, hemp may shrink like linen. Once hemp fabric shrinks, it becomes stable and cannot shrink any more. Any shrinkage is reduced by using cold water.
Why is hemp fabric more expensive than cotton?
Hemp is more expensive as it is grown on a considerably smaller scale and it needs special processions. The limited number of suppliers and the history of legal limitations continue to make the prices of hemp high. Hemp will potentially become cheaper with the increase of demand and the loosening of regulations.



