Cotton cultivation ranges from Asia to the Americas. Learn how China, India, United States, Pakistan, Brazil, and Uzbekistan have contributed to the global production of cotton and how this crop contributes to industries, trade, economies, and daily life. Cotton is universally acknowledged to be one of the most important crops grown. In one way or the other, cotton is utilized daily around the world. Natural fibers make every soft shirt and every cozy blanket, taking a significant role in the comfort of people and in the economy. Cotton production is a multifaceted sector that extends to the cooperation of people and entire nations. To fully appreciate the modern world, one must consider the history of cotton and it produced.
Why Cotton Still Matters Today

Cotton cultivation and use is estimated to have began more than 5000 years ago. Ancient civilization such as India, Egypt, and America practiced cultivating the plant for the sole purpose of trading and clothing. Cotton’s worldwide distribution as a result of global trading has made it a necessity to the economy today. Rich and poor nations alike have benefitted from the global demand, as it has led to the creation of thousands of jobs.
Ideal Conditions for Growing Cotton

Cotton plants prefer a warm and sunny climate. They require a long summer, rich soil, ample water, and sunlight. Excessive rainfall is harmful, and drought lowers yields. Cotton grown in tropical and subtropical regions are often very successful because of these conditions. Farmers in these regions are able to manage irrigation and pests for optimal crop yields. These attempts are a testimony to the importance of climate in conjunction with farming proficiency.
Leading Cotton Producing Countries
Cotton Production in the US
The US is still one of the top producers of cotton in the world. Texas, Georgia, Mississippi, and Arkansas are some of the most important regions. US cotton comes from large scale dryland farms with sophisticated farming machinery. Farmers are able to quickly harvest large patches of land within a short amount of time due to enhanced cotton harvesters. A large portion of the cotton is exported, and the country’s position in international trade is very important. It also helps sustain employment and income for people living in farming towns.
Cotton in India
The Indian legacy of farming cotton is centuries old. Indian farmers grew cotton which was being traded throughout Asia and Europe. India is one of the first cotton producers in the world. Gujarat, Maharashtra and Punjab are known to be indias cotton farming states. The cotton grown in India is used in the production of textiles, used in India and exported to other nations. Farmers in this region rely on irrigiated and monsoon rainfall for production.
Cotton in China
Xinjiang is known to be the capital of farming cotton in China. China produces large amounts of cotton for the world which is then used in textiles, fabrics, clothing, and household goods. China is one of the biggest producers of textiles, leading the world in the domestic demand for cotton. Because of this, China is a low importer of cotton. The farming and industrial sectors in China works together to make the economy boom, keeping cotton the center of focus.
Cotton in Pakistan
Similar to much of the world, cotton farming in Pakistan also plays a key role in supporting the economy. The Punjab and Sindh provinces are organized in the cotton farming regions. Cotton are not only enables local farmers, supporting the local economy, but also textile mills as well. Pakistan pampers world with its fabric and garment. The economic significance of the crop is such that is often dubbed as “white gold”. The crop single handedly supports millions of families.
Cotton in Brazil
Brazil, like Pakistan, is also a fast growing nation in cotton production. The country is one of the largest land and has favorable climate, which is why cotton is grown in Brazil. Cotton are mostly exported to Asian countries that have a high demand. Unlike other countries that still rely on subsistence farming, Brazilian farmers are using advanced farming which increases yield and decreases wastage. This new farming industry enables Brazil to rival with the other cotton leaders such as India and China. The Brazilian economy is also gaining dominance in international trade.
Cotton in Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan continues to be one of the leading producers of cotton in Central Asia. It has done so since decades, and they remain both a global exporter and a reputable company for the manufacturing of cotton. This cash crop cotton has primarily driven the economy in these regions, along with changing the culture and lifestyle of rural communities. Uzbekistan cotton has also undergone progressive changes in how the crop is harvested in order to minimize the water used and maximize the productivity of the crop, and in doing so still continues generating income from cotton. Uzbekistan cotton still serves as national pride to the country.
Cotton in African Countries
African nations also participate in the global cotton market, where countries such as Mali, Benin, and Burkina Faso regard cotton cultivation as a primary cash crop and dominate the region’s production. Cotton from Africa is primarily sent to other regions of the world for sale, with local communities surrounding the farmers of these nations relying on the income produced from these exports. Falling prices and unreliable weather conditions greatly harm the farmers in these regions. Despite these trials, cotton is still a primary source of income for most families in Africa.
Cotton and Global Trade

As one of the most notable traded crops worldwide, Cotton’s significance in the economy has indeed evolved. Its unique cultivation and the processing of its fibers, with the current business lines of its byproducts woven in, come with geospatial variations and inter-country economic zoning. Transnational economy interlinkages are a true demonstration of advanced global economics. Exported cotton has more benefits than just economic independence and global interdependencies; the elasticity of demand in several industries, particularly agriculture and textiles grows with every unit produced.
Cotton and Modern Technology

Unlike several centuries ago, the practice of farming has definitely undergone a revolution. Thanks to modern and advanced tools such as tractors, harvesters, and irrigation systems, the effectiveness of farming has drastically improved. Even the farming of cotton, which has been criticized for its low output, has been proven to give better yields and improved quality when modernized farming techniques are used. The increased productivity of farming has recently been attributed to better techniques used in the management of farming and the innovative development of nurturing systems for seedlings.
Cotton and Sustainability

Perceptions towards the environment have shifted and have started to have an impact on agrarian practices. On large scale farms, cotton production usually requires large quantities of water and numerous chemicals, which contribute to the pollution of soil and water bodies. Given this, a large number of farmers have started utilising sustainable techniques, and those which include organic farming, drip farming, and biological pest management. These techniques preserve the environment while also allowing cotton to thrive and grow. Sustainability is the future of cotton farming.
Cotton in Everyday Life

It is in abundant supply, and is often taken for granted. Cotton is a component of the shirt and the towel. It is is used to make other products such as jeans, socks, bed sheets, and numerous others. Even band-aids and cotton buds originate from this agricultural product. Natural fibers such as cotton rank high due to its softness, strength, and adaptability. Everyday life without cotton would be a rather stark contrast.
How Cotton Helps Economies
The cultivation of cotton is an economic mainstay that extends beyond the confines of agriculture. The income generated by cotton farming transcends multiple continents as it provides employment to farmers, traders, and even mill workers. Countless families in countries such as India, Pakistan, and Indonesia rely solely on cotton farming in their day-to-day lives. The infrastructure that is subsequently constructed uses the debt that is acquired through exports. Such a crop proves to provide more than just materialistic fabric, it provides economic prowess.
Challenges for Cotton Farming
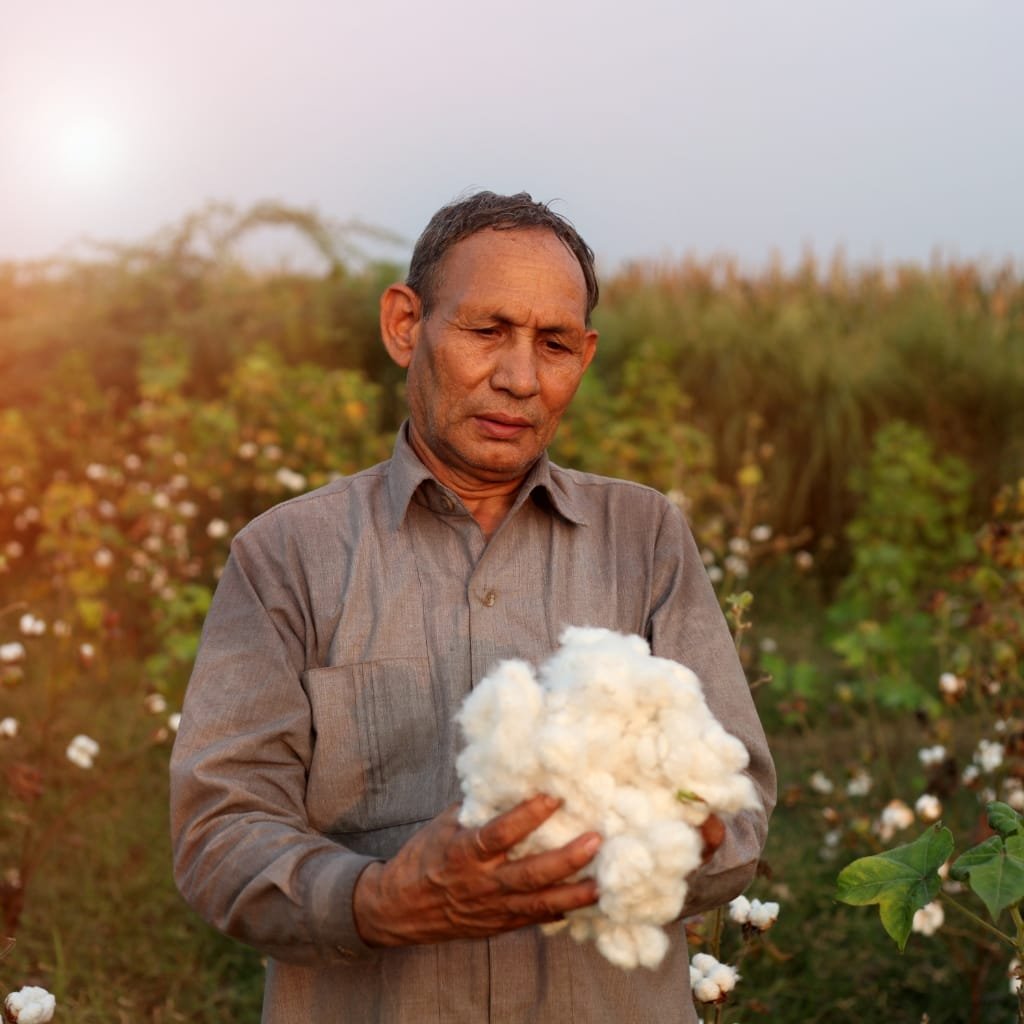

The positive aspects of cotton farming regarding economy and employment opportunities is undeniable, however, the farming of cotton does have its negative aspects too. Due to the constant shifting of weather patterns, harvests are impacted and crops susceptible to pests, face possible extinction. Reliable irrigation is key for cotton farms in drought-prone areas. If farmers and workers are careless, their income earned may suffer-falls global prices. The excessive use of water in some countries is a dominant concern. These issues are a product of a lack of planning that are easily resolvable with contemporary technological advancements and international cooperation.
Cotton Farming’s Tomorrow
The future of cotton farming, as well as cotton itself, appears both promising and challenging. Farmers growing cotton numerous decades from now will need to incorporate farming mechanisms which accommodate to climate change. Farmers may primarily use genetically modified seeds to suit their farming needs. Ecofriendly farming will only increase in popularity. The demand for cotton products will greatly increase as its comfort and natural feel becomes even more appreciated. More refined farming practices will only assist the plentiful cotton farming.
Conclusion
The world prospers from cotton as more than a mere crop. The product serves as a more intricate link between diverse countries, industries, and families as well. The product’s composition in China, India, the United States, Pakistan, Brazil, and even Uzbekistan shows its global reach. Cotton serves to continuously drives trade, culture, as well as a means of income from the fields of Africa all the way to the growing, flourishing farms in the United States. From soil all the way to fabric, the crop represents tremendously intertwined resilience, progress, as well as connection. Its importance in the world may even grow more than it is now, as one way or the other the world’s frost will be felt in the industries and little communities as well.
Read more Cotton Fabric? Its Properties, Production, and Uses
FAQs
Which country produces the most cotton today?
China and India lead the world, followed by the United States and Pakistan.
Why does cotton grow better in hot regions?
Cotton needs long summers, sunshine, and fertile soil to grow well.
How does cotton farming support economies?
Cotton produced worldwide provides jobs, trade income, and industrial raw materials.



