Cotton fabric reigns as one of the most widely used and adaptable fabrics across the globe. It’s well known for its breathability and relative affordability. Cotton has served as a staple for clothing and home textiles for ages, and can be seen in the form of a casual T-shirt, luxurious bedsheet, or a durable pair of jeans. What most people may not realize is there is more to this humble fiber than meets the eye.
The History of Cotton Fabric

As far as the history of cotton fabric is concerned, it began more than 7,000 years ago. Archaeologists have located the presence of cotton in ancient civiliations such as the Indus Valley (modern day Pakistan and India) where the population began spinning and weaving cotton cloth as early as 3000 BCE.
Cotton farming later expanded to Egypt, which began to value it for its luxurious texture. Arabs began introducing cotton to Europe in the 9th century. Cotton was in high demand all around the world by the 17th century, which aligned perfectly with the Industrial Revolution as it mechanized the production of cotton.
The cotton gin revolutionized the cotton farming industry in the US around 1793 which caused an increase in production. Although the uptick in production was positive, it came hand in hand with the dark reality of increasing exploitation of enslaved people. Regardless of the obstacles the industry has seen, it is still one of the most impactful parts of the economy worldwide.
What Is Cotton Fabric?

Cotton fabric refers to the soft and fluffy fiber that develops around the seeds of the cotton plant. It is easier to manipulate cotton and the various products a person can create with cotton is maybe the reason a majority of the world’s population utilizes cotton products.
The fiber is spun into yarn or thread and is then woven or knitted to create a soft and durable piece of fabric. This material is absorbent in nature thus is ideal for a variety of uses, whether clothing or home textiles.
Where Can We Use Cotton Fabric?
Cotton fabric is one of the most popular textiles across the globe, valued for its comfort, strength and soft nature. The cotton fabric is well known for the comfort, soft nature, and ease of use. This is the reason the use of cotton is at the core of a variety of industries, and can be seen in a wide range of products that each of us uses in our day to day life.

Clothing
The breathable and soft fabric, cotton, is a staple in the fashion industry. It is used in the manufacturing of t-shirts, shirts, blouses, and even skirts and dresses. Underwear, socks, and bras are also made of cotton due to its softness and moisture-absorbing properties. Comfortable and durable, jeans and casual trousers are made with cotton. Children’s clothing is often made with cotton due to the fabric’s gentle and non-irritating feel on sensitive skin. Cotton serves as an essential year-round. It is used in summer wear as well as layering pieces for winter.
Home Textiles
In home furnishings, cotton fabric is ubiquitous. Bed sheets, pillowcases, and duvet covers are made from cotton because of its softness and moisture regulation. Cotton towels are also highly absorbent making them ideal for bathrooms and kitchens. Drapes and curtains made of cotton have an elegant softness and are easy to launder. In upholstery, cotton is often blended with other fibers to improve the durability and comfort of home furnishings. Because cotton blends luxury and practicality, it is highly sought for home textiles.
Medical Supplies
The healthcare sector depends on cotton extensively because it is hypoallergenic and absorbent. Cotton is used to manufacture bandages, gauze pads, cotton swabs, and even surgical masks. These items need to be made from soft and safe materials that can absorb fluids, and cotton fulfills these requirements. Cotton is sterilized and packed in first aid kits and hospital supplies all over the globe.
Industrial Uses
Cotton also has other important uses in industry aside from clothing and textiles. Heavy cotton fabrics including canvas and denim are used in the manufacture of rugged goods like tarpaulins, tents, sails and bags. Cotton is also used in the form of workwear for construction, farming, and manufacturing, where strong but breathable uniforms are needed. Its strength, combined with comfort, makes cotton perfect for tough environments where resilience and breathability are required.
Personal Care Products
The soft texture of cotton makes it ideal for personal care items. For safety and efficacy, pure cotton is the material of choice for more delicate items such as cotton balls, facial wipes, and cosmetic pads. During skincare routines, cotton rounds are used to apply toner or remove makeup. Hygiene products such as cotton swabs and sanitary pads are also made with cotton due to its absorbent and skin-friendly properties.
The versatility of cotton fabric makes it an essential in many parts of a person’s daily life. Casual and business clothing, as well as medical apparel, and even home décor and industrial textiles all make use of cotton. The fabric’s natural comfort coupled with its ease of maintenance and ability to be used in multiple products makes it ageless and used around the world.
The Making Process of Cotton Fabric
The fabric creation journey of a cotton plant involves a series of steps.

1. Cultivation and harvesting.
Cultivation and harvesting process starts in the fields with cotton plants which are grown in a warm, sunny climate with enough rainfall or irrigation. The largest cotton-growing regions include India, China, the United States, and Pakistan. Following sowing, the cotton plants grow and are accompanied with blooming flowers. These flowers then form seed pods, which are called bolls. These bolls contain seeds alongside soft, fluffy cotton fibers.
The ripened bolls of cotton indicate it’s time to harvest. In some places, cotton is still harvested by hand to reduce damage to the fibers. Yet, in large-scale commercial farms, mechanical harvesters do the work to collect large amounts of cotton efficiently. It is important to to do harvesting in a careful and considered manner to ensure the quality of the fibers is retained. Too much machine handling will break or damage the fibers.
2. Ginning
After harvesting, a cotton gin is used to separate the cotton from the seeds, leaves and other debris. Ginning is a very delicate procedure and needs to be taken care of. In the past, ginning was conducted by hand, until in 1793 Eli Whitney introduced the machine cotton gin, which sped the process up significantly.
Cotton bolls undergo a process in which rollers and saws pull the fibers from the seeds. This process leaves the bolls clean of the shredded lint and seeds, making it possible to be used for cottonseed oil or animal feed. Proper ginning is important to maintain the quality of the cotton which is crucial for the spinning of the yarn.
3. Spinning
After completing the ginning process, the cotton fibers are sent to a spinning mill. Spinning separates the fibers into the loose, pliable, and separated strands of yarn. First, the fibers are carded, which is a process that removes any remaining impurities or short fibers.
Afterward, slivers are drawn out and twisted together as a part of the spinning step. This step is significant to the yarn as twisting it makes it strong and flexible. Depending on the fabric that is to be produced in the end, the yarn’s thickness, texture, or strength can be modified. To obtain superior and diverse quality and texture of yarns, more advanced spinning techniques such as ring spinning or open-end spinning can be utilized.
4. Weaving or Knitting
Once the yarns are completed, the next step fabric formation which is either weaving or knitting.
Woven fabric production is the oldest form of fabric production, and it is created by interlacing the two lines of yarns, referred to as warp (lengthwise threads) and weft (crosswise threads) at a right angle on a loom. Some of the woven fabrics produced using this method are denim, poplin, and twill. The fabric’s strength and texture can also be determined by the tightness of the weave.
The act of knitting naturally creates fabrics like jersey and interlock knits, which are more stretchable and flexible compared to other fabrics. Cotton knits are common sewing materials for T-shirts, undergarments, and athletic wear because of their comfort and flexibility.
Both weaving and knitting can be done by hand in small-scale workshops or by automated machines in large textile mills. The choice between these two methods depends on the desired fabric characteristics.
5. Dyeing and Finishing
The dyeing process, in which fabrics are treated with natural or synthetic dyes, is one of the most important final steps. Cotton is particularly easy to dye and, therefore, can be produced into many different fabrics.
Manufacturers may also print cotton fabrics after dyeing them, using screen printing, digital printing, or block printing to apply various designs, patterns, or logos. In the final steps, they apply multiple finishing processes to enhance the fabric’s softness, wrinkle resistance, water repellency, and even stain resistance.
Some of these processes are readily available and include:
- Mercerization: Treatment with caustic soda increases luster and strength.
- Sanforization: The process of pre-shrinking the fabric to make sure it does not shrink in the future.
- Brushing: Softer to the touch as a result of raised surface fibers.
After completing these procedures, quality control teams inspect the finished cotton fabric, roll it onto bolts, and schedule it for shipping to manufacturers who will turn the fabric into garments, home textiles, or other cotton-based products.
Leading Cotton Producing Countries
Cotton is a strategically important crop grown in every part of the world for it serves the textile and clothing industry. However, a small number of countries are the most important cotton producers and control the entire value chain starting from raw fiber to the garments. These countries not only produce significant amounts of cotton but also perform a major function of processing and trading cotton and its products.
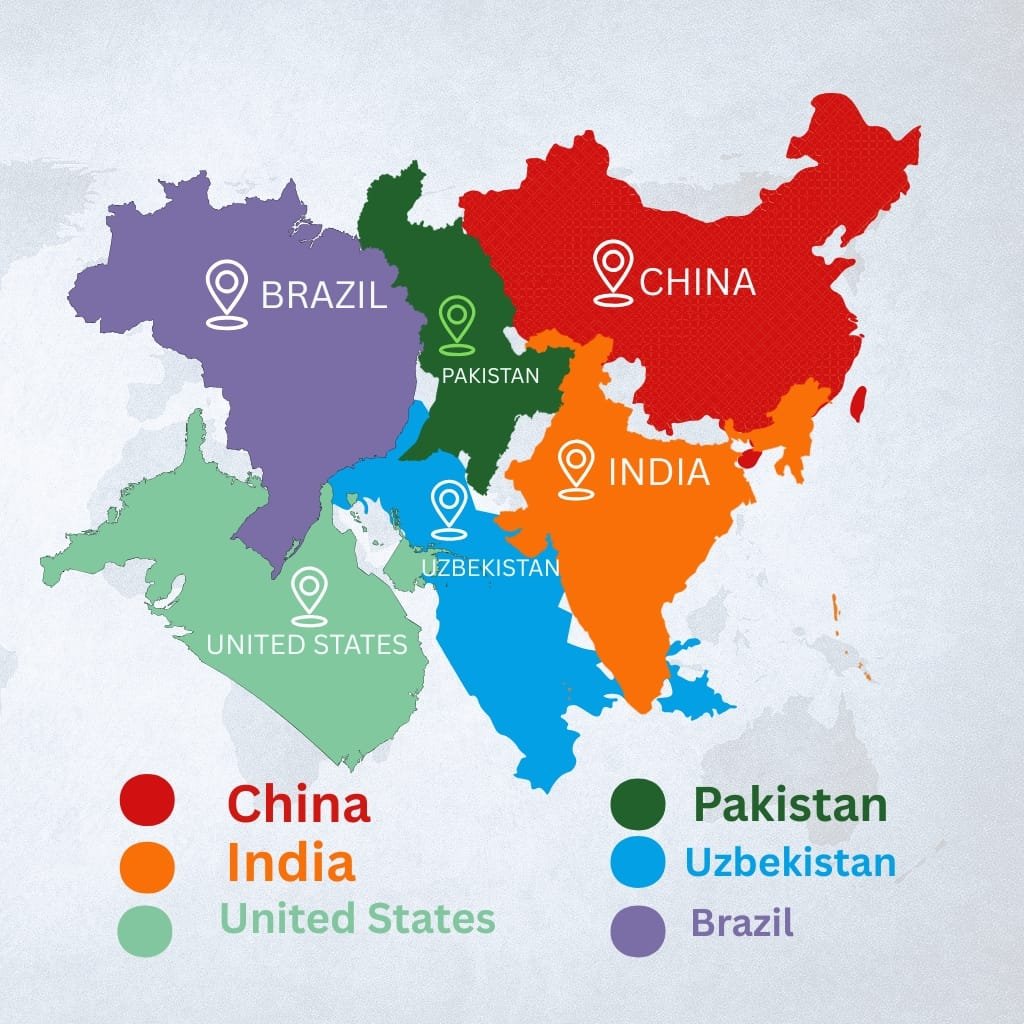
China
China is one of the largest producers and consumers of cotton in the world. The cotton growing area in the north west of the country, the Xinjiang region, is the cotton producing area of the country, where more than 80% of China’s cotton is produced. China is also leading the world in textile industry as there are thousands of plants. That convert cotton to yarn, fabric and garments. The country has a vertically integrated cotton industry from farming and up to the final products which makes it an important player in the cotton industry. Moreover, China is increasing its domestic consumption of cotton products because of the rising middle class and growing domestic fashion industry.
India
India remains the globe’s foremost producer of cotton, holding a prominent share of its production. Indian farmers cultivate cotton across vast areas in states such as Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Andhra Pradesh. A distinguishing mark for India is its smallholder farming system, which features millions of farmers in the country’s cotton production. India is also a significant supplier of cotton yarn and textiles, boasting a developed spinning and weaving industry. India’s reputation, especially in eco-friendly markets, is enhanced by its history of handloom and organic cotton production.
United States
The United States still holds its position as one of the leading exporters of cotton and one of the largest suppliers of raw cotton fiber. Farmers primarily grow cotton in the southern states, especially in Texas, which produces nearly half of the country’s total output. Textile mills around the world highly demand USA cotton because of its superior quality and uniformity. Additionally, American farmers use precision farming and other advanced mechanized technologies to boost productivity and increase farm output. Moreover, the USA is one of the frontrunners in advocating for responsible practices in the production of cotton with the U.S. Cotton Trust Protocol.
Pakistan
Pakistan is famous for its colorful textile industry, which is essential to the economy. The country is one of the top five cotton producing nations of the world and Punjab and Sindh are the provinces which grow the crops. Pakistan’s cotton serves its large spinning, weaving, and garment manufacturing industries which, in turn, are among the leading exports of the country. Pakistan is still an international cotton and textile manufacturing center. Because of its skilled workforce in textiles, even though the country faces severe droughts and primitive farming techniques.
Brazil
Brazil is an emerging worldpower in cotton production. Within the last 20 years, the country’s cotton production has increased largely due to the adoption of new technologies along with large scale farming. The cotton grown in the country’s central-western states like Mato Grosso is planted in the large areas which are easy to mechanize and provide good yields. Brazil has become one of the top marketers of cotton lint and raw cotton is supplied to textile mills in Asia and Europe. These developments alongside the country’s sustainable farming policies and raw material has strengthened its international position.
Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan is well known for longstanding historical reasons as a sizable producer of cotton which is commonly referred to as “white gold”. The country boasts significant yields of cotton along with extensive irrigated fields, placing it as a notable producer on the world stage, as well as within the country, the cotton economy supports millions in the farming and textile industries. In the past, the country has been known to face PR issues for its labor practices, but recently, it has sought to rebrand its image by implementing modern practices, banning forced labor, and striving for sustainable farming tenets.
These countries form the backbone of the global supply chain for the commodity. Their input is significant in the production of raw cotton. In addition to cultivating, these countries have a great role in processing and determining the yield for export quality textiles which are in great demand. The cotton production dynamics of these countries also affect the value of cotton, its trade guidelines as well as the policies concerning its production and trade.
Types of Cotton Fabric
There are many different types of cotton fabric, from simple and basic to luxurious. Each type of fabric has its different textures, qualities and its intended use. Having in mind the wide range of uses, it is essential to understand the different types of cotton fabric.

Upland Cotton
Upland cotton is both the most commonly produced and most readily available cotton fabric worldwide. It comprises about 90\% of the world’s cotton production. Upland cotton fabric has short to medium-level fibers and is relatively inexpensive. As such, it is used to make casual clothing such as t-shirts and jeans, as well as other household items. While it primarily serves as a mass-produced textile, it is still more durable when compared to other garments. It is also more affordable than a premium cotton garment.
Egyptian Cotton
Egyptian cotton is also cultivated along the banks of the Nile river. This type of cotton fabric is well-known as one of the finest cotton fabric because of its soft and durable features. It is also extremely soft to the touch, compared to other cotton fabrics. Egyptian cotton fabric and other luxurious materials are often made into extraordinary garments, towels, and bedsheets. It is a common misconception that Egyptian cotton and other luxurious materials are one-time use fabrics. Due to its softness, it is often used in home textiles and other premium items because it becomes softer after every wash.
Pima Cotton
Pima cotton is another premium variety fabric for its softness, sheen, and strength. It is primarily grown in the United States and Peru. Pima cotton has long staple fibers similar to Egyptian cotton, which provides it with a silky texture and makes it more durable. Blocks and dresses made from Pima cotton fabric withstand pilling, and color and shape retention is observed even after multiple washes. It is also common in high-end dress shirts, blouses, and T-shirts due to the durability and comfort they provide.
Organic Cotton
Organic cotton fabric is produced without the application of artificial pesticides, herbicides, or GMOs. This type of cotton is organic in nature and aids in sustainable farming without compromising the environment. It is favored by a wide range of consumers who buy sweatshirts, bedsheets, and clothing for infants because it is skin-friendly and doesn’t harm the environment. Organic cotton is quickly becoming a must-have for eco-friendly clothing collections as the demand for sustainable fashion increases.
Supima Cotton
Supima cotton is a registered name for an enhanced fabric type of pima cotton grown solely within the United States. The term “Supima” is short for “Superior Pima” which captures the cotton’s claim to fame of having unrivaled durability in comparison to other cottons, unprecedented cotton softness, and exceptional color retention when compared to other cotton fabric types. Supima cotton fabric is smooth to the touch, is treasured for its lavish smooth texture, and is durable over time, making it a preffered option for luxury clothing, bedding, and bath linens. Supima Cotton stands out among the upper-tier cotton types due to its enhanced weave, brighter hues, and stronger resistance to pilling.
Cotton Lawn
Cotton Lawn is a type of cotton fabric that is lightweight and has a shighter weave making it smoother and crisper. The fabric’s warmth, softness, and breathability makes cotton lawn a frequent choice for summer dresses, blouses, and children’s clothing. Cotton Lawn’s semi-sheer make it perfect for creatively layered garments that require a hint of delicacy and softness, and for use in layered garments and delicate accessories. Designers greatly appreciate the drape of cotton lawn fabric because it contours to the body and offers both comfort and elegance in casual and formal wear.
Cotton Sateen
The cotton sateen fabric is smooth and glossy owing to a specialized weaving technique known as sateen weave. This cotton type fabric is typically utilized for a more luxurious bed and pillow covers as well as formal gowns. Cotton sateen replicas the glossy look of silk; however, it is more breathable and easy to maintain. The look is polished and the fabric’s soft silk like appearance add class to the home textiles and fashion accessories.
Cotton Denim
Cotton denim is a type of cotton fabric widely used for, and a staple in, casual wear, especially jeans, jackets and skirts. Denim cotton has a twill weave, a type of weave that shows a diagonal ribbing. Denim is known for its a rugged texture and long-lasting strength, which makes it a fabric of choice over time. With wear and washing, denim becomes softer and develops a unique patina which substantiates its aesthetic value. Cotton denim continues to be a staple in casual fashion because it blends timeless style, comfort, and rugged durability.
Certification Types for Cotton Fabric
As with all products, cotton products undergo various certifications to ensure ethical and sustainable production practices.
1. GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard)
Certifies organic fibers and environmentally responsible processing.
2. OEKO-TEX Standard 100
Ensures textiles are free from harmful substances.
3. Better Cotton Initiative (BCI)
Focuses on improving global cotton farming practices.
4. Fairtrade Certified Cotton
Promotes fair wages and ethical labor practices for farmers.
5. USDA Organic
Certifies organic cotton grown in the USA.
Environmental Impact of Cotton Fabric

The impacts of the fabric type are more on the positive side due to it being natural and biodegradable. The more negative side comes from the conventional cotton farming practices due to the large amounts of water consumed. nd the pesticide usage which is harmful to the ecosystems.
Farmers and producers are mitigating the environmental impacts of drip irrigation and integrated pest management techniques by adopting organic cotton and more sustainable farming methods. Organizations like BCI and Fairtrade are also driving eco-conscious efforts in the cotton industry.
Cotton: The Softest and Cheapest Fabric in the World
People often consider cotton the softest and most affordable casual fabric. Its easy availability, widespread cultivation, and capacity for mass production make it a popular choice for the masses. Despite that it is inexpensive, it is a soft fabric. Cotton continues to be a first choice for soft, comfortable, and inexpensive fabric which is breathable.
Conclusion
Cotton fabric is a backbone of the textile industry because of its softness, ease to tailor, and inexpensive price. This fabric has been around since centuries and its journey continues to fascinate with modern eco-friendly innovations. No matter the fabric a person wishes to wear, be it for comfort, style, or environmental impact, cotton stands out every time.
FAQs
Is cotton fabric breathable?
Yes, cotton is highly breathable, making it ideal for hot and humid climates.
Can cotton fabric shrink after washing?
Yes, unless pre-shrunk, cotton tends to shrink when washed in hot water.
Is organic cotton better than regular cotton?
Organic cotton is better for the environment as it’s grown without synthetic pesticides and uses less water.



